How to Eat When You Have Type 2 Diabetes
•Posted on April 17 2024

Diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes, a condition characterized by insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
With the prevalence of diabetes on the rise globally, understanding how dietary choices influence the course of the disease is crucial for effective management and prevention.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricate relationship between diet and type 2 diabetes mellitus, explore dietary recommendations, and address common questions surrounding the condition.
Recommended for You:

How Does Diet Affect Diabetes Mellitus?

Diet for Diabetes Mellitus
A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for individuals with diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes.
Key dietary principles include:
-
Carbohydrate Control: Monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Focus on complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, while limiting refined sugars and processed foods.
-
Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating and fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Opt for smaller, frequent meals to help regulate blood sugar throughout the day.
-
Healthy Fats: Incorporate heart-healthy fats from sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil into your diet while limiting saturated and trans fats, which can contribute to insulin resistance and cardiovascular complications.
-
Lean Protein: Choose lean sources of protein such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes to help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote satiety.
Related Post: How to Balance Blood Sugar Levels Naturally
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

Can Type 2 Diabetes Kill You?
Untreated or poorly managed type 2 diabetes can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and nerve damage, which can be life-threatening if left unchecked.
However, with proper medication, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to a healthy diet, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively manage the condition and reduce their risk of complications.
What Level of Blood Sugar is Dangerous?
Blood sugar levels that are consistently elevated above target ranges pose a significant risk to health.
While specific thresholds may vary depending on individual circumstances, blood sugar levels exceeding 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) after meals or fasting blood sugar levels consistently above 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L) are generally considered dangerous and warrant medical attention.
Recommended for You:

What Are the 4 Types of Diabetes?
There are four main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in insulin deficiency.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form of diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency.
- Gestational Diabetes: A type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth, although it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Prediabetes: A precursor to type 2 diabetes, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that are not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Without intervention, prediabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes.
Related Post: Are Skin Tags a Sign of Diabetes?
What is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
The main differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes lie in their underlying causes, onset, and treatment approaches:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Caused by autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells, typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Caused by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, usually diagnosed in adulthood, managed with lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and/or insulin therapy.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

How Do I Know If I Have Type 2 Diabetes?
Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Recommended for You:

How to Cure Type 2 Diabetes Permanently?
While there is no cure for type 2 diabetes, it can be effectively managed and even reversed through lifestyle modifications such as:
- Adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity to promote weight loss and improve insulin sensitivity
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adhering to prescribed medication regimens
- Managing stress and getting adequate sleep to support overall health and well-being
Exploring the Role of Magnesium in Diabetes Management

Can Greenway Biotech Magnesium Help With Diabetes?
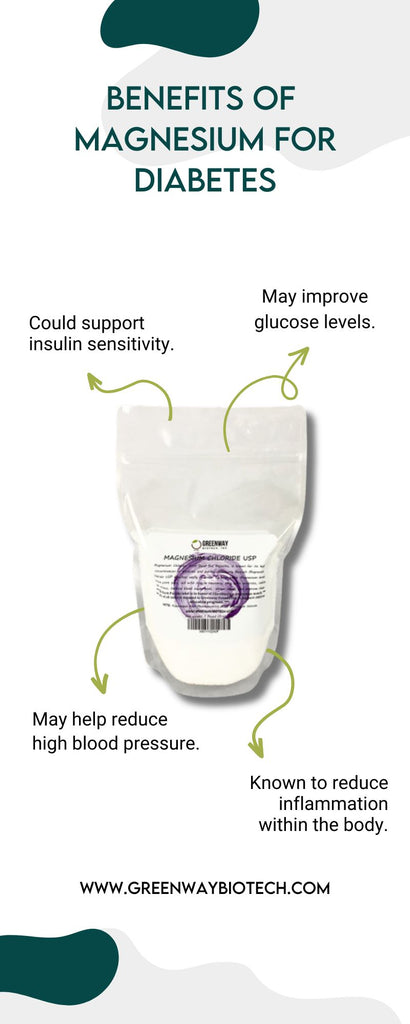
Magnesium plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, making it an essential nutrient for individuals with diabetes mellitus.
Greenway Biotech offers high-quality magnesium supplements that may help support diabetes management by promoting optimal magnesium levels in the body.
However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have diabetes or are taking medications for the condition.
Related Post: Magnesium and Diabetes
Navigating the Path to Diabetes Management
In conclusion, diet plays a central role in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus, influencing blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and overall health outcomes.
By adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively manage the condition, reduce the risk of complications, and improve quality of life.
Through medication management, regular monitoring, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can take control of their diabetes and embark on a journey toward better health and well-being.
Comments
0 Comments
Leave a Comment